If your HVAC system isn’t performing as expected, it might be due to a faulty thermal expansion valve (TXV). This small but crucial component regulates the flow of refrigerant, impacting the system’s efficiency. Let’s delve into the common signs that indicate your TXV might be acting up.
Are you having trouble with your air conditioner and suspect a problem with the TXV? This guide will help you understand the signs of a bad TXV and how to check for it.
Signs of a bad TXV include high superheat, low superheat, high subcooling, low suction pressure, and low head pressure. To be sure that other problems aren’t the source of these symptoms, it’s crucial to take additional precautions.
The good news is that there are solutions at your fingertips.
How does a TXV valve work?
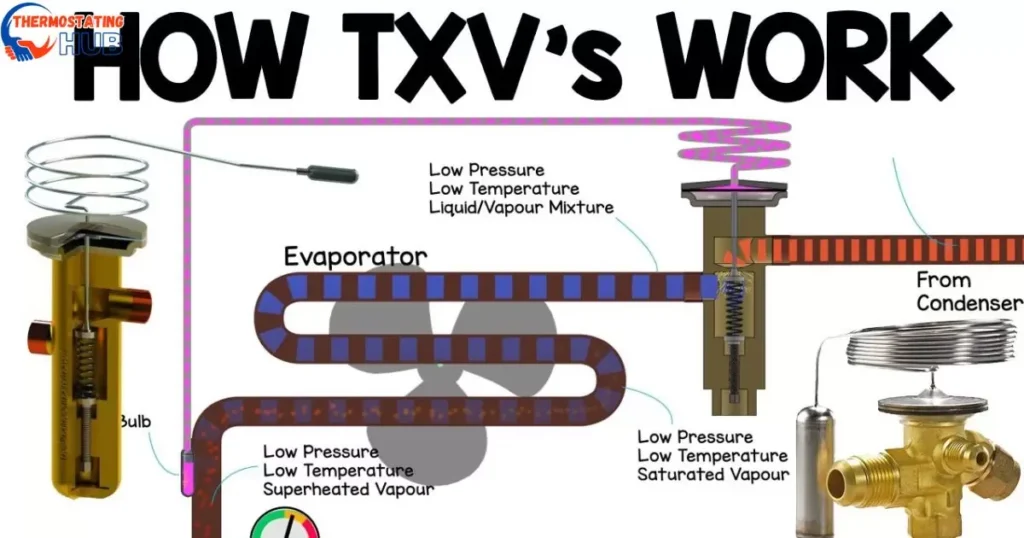
The TXV is like the traffic cop of your HVAC system, controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. It ensures the right amount of refrigerant enters, allowing for optimal cooling. Understanding this valve’s role is key to identifying potential issues.
For those who might not be familiar, let me quickly explain what a TXV is. A TXV, which stands for thermostatic expansion valve, is like a mechanical traffic controller for your air conditioning system. It’s responsible for making sure the right amount of cooling stuff (called refrigerant) goes into the part of the system that makes the air cold (evaporator coil).
This valve has a few parts, such as a sensing bulb, diaphragm, valve body, and valve seat. The sensing bulb is connected to the suction line of the system, and it checks how hot or cold the cooling stuff is before it enters the part that cools the air (evaporator coil). The goal is to keep things just right by controlling how much cooling stuff goes in.
What are the symptoms of bad TXV?
Now that we know what a TXV is, what signs should we watch for if we think there might be a problem with it?
High superheat
If your system is struggling to cool your space, high superheat might be the culprit. This means insufficient refrigerant is reaching the evaporator coil, leading to reduced cooling efficiency.
A broken thing in your HVAC system called the thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) can make the system not work well. It does this by not letting enough refrigerant go into the evaporator coil, which is a crucial part of cooling. The TXV’s job is to control how much refrigerant goes into the coil based on the temperature and pressure inside.
Sometimes, if there are bad things like dirt or water in the HVAC system, they can reach the TXV and make it not work properly. This means it might not allow enough refrigerant into the coil, making something called superheat go up.
Superheat is when the refrigerant gas leaving the coil is hotter than it should be. If this happens a lot, it means there’s not enough refrigerant turning into gas in the coil. This can make the cooling power go down, and the system won’t work as well.
Read also: Sensi Thermostat Not Turning On AC [Fixed]
Low Superheat
Conversely, low superheat indicates an excess of refrigerant in the evaporator coil. This can cause the system to work harder than necessary, affecting overall performance.
A faulty thing called a thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) can make an HVAC system not work well. It happens when too much of the cooling stuff (refrigerant) goes into a part called the evaporator coil.
Sometimes, if there are dirty things in the system, they can make the TXV stick open. This means it lets in too much refrigerant, which is also called overfeeding. Bad insulation on the valve can also make this happen.
When there’s too much refrigerant in the evaporator coil, it makes the refrigerant leaving the coil too cold. This is not good and can mess up how the whole system works. It’s important to fix this problem to keep everything running smoothly.
High subcooling
When the liquid refrigerant leaving the condenser is too much, it can result in high subcooling. This puts unnecessary strain on the compressor and can lead to system failure.
A bad TXV in your HVAC system can make the refrigerant flow into the evaporator coil too slow. This occurs when debris, moisture, or an inadequately sized metering device obstructs the TXV. This slow flow can lead to too much liquid refrigerant backing up in the condenser coil, causing what’s called high subcooling.
Having high subcooling is not good because it can make your HVAC system less effective at cooling. It can even harm the compressor and increase the chance of too much liquid refrigerant going into the compressor. Besides a faulty TXV, other things like a dirty condenser coil or not enough air over the condenser can also make subcooling too high. Keeping these things in check helps your HVAC system work better.
Low suction pressure/low head pressure
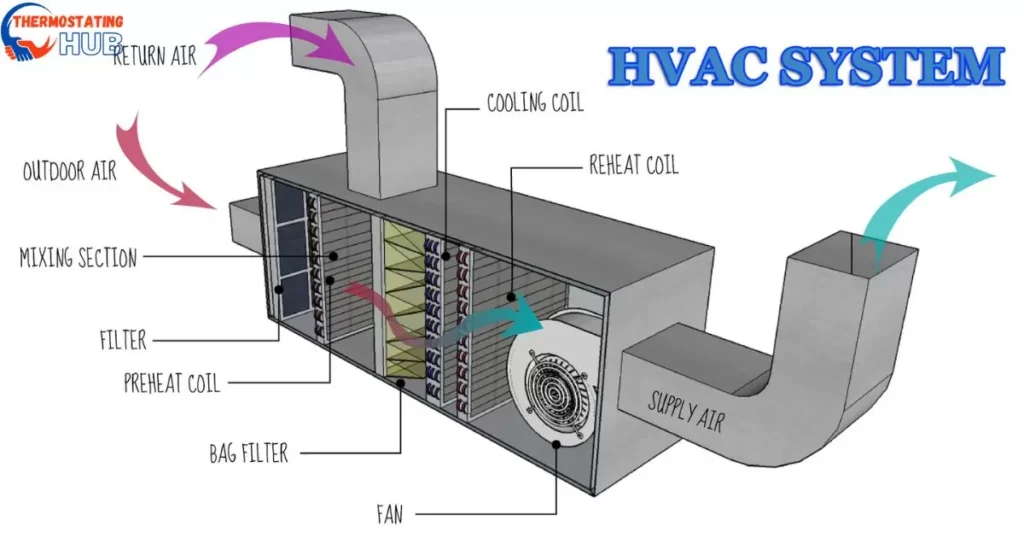
Issues with the TXV can also manifest as abnormal suction and head pressure. Low suction pressure means not enough refrigerant is returning to the compressor, affecting the entire cooling process.
A faulty TXV can make an HVAC system not work well by slowing down the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil.
When the TXV isn’t working right, it might block too much refrigerant from going into the evaporator coil. This makes the suction pressure drop because there isn’t enough refrigerant in the suction line. The head pressure also drops because the compressor doesn’t get enough refrigerant to compress and send to the condenser.
Low suction pressure and low head pressure can make the system cool less, use more energy, and make the compressor wear out faster.
A bad TXV might also happen if there’s a problem with the bulb tube rubbing against something or if there’s an external equalizer without a core depressor on a port with a Schrader core.
But just having these issues doesn’t automatically mean your TXV is bad. You might need to do more checks to figure out if the TXV valve is the problem. We’ve listed the steps and process for diagnosing a TXV below.
How to properly diagnose a TXV valve
Diagnosing a problematic TXV involves checking superheat and subcooling values, along with suction and head pressures. A skilled technician can use these readings to pinpoint issues and determine if the TXV is causing the system’s inefficiency.
- Check refrigerant levels and temperatures on both ends of a split system.
- Ensure a full line of liquid before the TXV with a specified subcooling of about 10°F.
- Verify subcooling outside, looking for consistent temperatures inside and out to rule out issues like kinked lines or plugged line driers.
- Confirm enough liquid pressure for a minimum 100 PSI difference between liquid line pressure and desired evaporator pressure.
- Note that low head pressure in low ambient conditions can affect the valve’s performance.
- Check the superheat at the evaporator outlet, aiming for 6-14°F; lower than 6°F may be overfeeding, and well above 14°F suggests a failed closed valve.
- Some valves may have a screen before them, causing restrictions; freeze the coil or use thermal imaging to identify the issue.
- The TXV is meant to maintain a consistent superheat, so identifying temperature drops helps diagnose problems.
Read Also: Bryant Furnace Code 33
Pros and Cons of Understanding Common Symptoms of Bad TXV
Understanding the common symptoms of a bad TXV comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, early detection can save money on energy bills, extend the life of your HVAC system, and prevent major breakdowns. However, the complexity of diagnosing TXV issues and the potential costs of professional repairs are important considerations.
To help you weigh these factors, here’s a simple table:
| Pros | Cons |
| Early Detection | Complex Diagnosis |
| Cost Savings | Repair Costs |
| Extended System Life | Dependency on Professionals |
This table provides a quick overview of the benefits and drawbacks, helping you make informed decisions about managing your HVAC system.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of a bad TXV?
Common symptoms of a bad Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV) include high or low superheat, high subcooling, abnormal suction and head pressures, and inadequate cooling performance. Any of these signs may indicate issues with the TXV affecting the refrigerant flow in your HVAC system.
How do I know if my metering device is bad?
If your metering device, like the TXV, is faulty, you may observe symptoms such as uneven cooling, poor system efficiency, and irregular temperature control. Additionally, monitoring superheat and subcooling values can provide insights into the proper functioning of the metering device.
What happens to an AC unit when the TXV goes bad?
When the TXV malfunctions, your AC unit may experience reduced cooling efficiency, uneven temperature distribution, and increased strain on the compressor. This can lead to higher energy consumption, higher utility bills, and eventually, potential damage to other components of the air conditioning system.
What are the first three things to check if a TXV is flooding?
If you suspect a TXV is flooding, check the following:
- Superheat Values: Evaluate if the superheat values are within the recommended range.
- Suction Line Temperature: Measure the temperature of the suction line; an unusually cold suction line may indicate flooding.
- Condenser Subcooling: Examine the subcooling values to ensure they are within the specified range. These initial checks can provide insights into potential flooding issues with the TXV.
Final thoughts
Keeping an eye out for these symptoms can help you address TXV issues promptly, ensuring your HVAC system runs smoothly. Regular maintenance and timely repairs by a qualified professional can extend the life of your system and keep your indoor environment comfortable. If you notice any of these signs, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional for assistance.
The TXV valve is important for making sure the air conditioner or heater works well by controlling the flow of cooling liquid. If you notice problems with the valve and fix them quickly, you can save money on energy and avoid expensive breakdowns. Regular check-ups by professionals can prevent issues with the valve and keep your heating and cooling systems working well.

I’m Nicholas Clark, your HVAC guide at thermostatinghub.com. More than just a writer, I’m your go-to guy for solving heating and cooling mysteries. My blog is a storytelling haven where we unravel HVAC tales together. Let’s turn your comfort queries into stories of warmth and coolness!